Gynaecomastia is a condition that causes the enlargement of male breast tissue, often leading to physical discomfort and emotional distress. While it is common and usually harmless, many men struggle with self-consciousness and uncertainty about whether they have gynaecomastia or another issue. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and diagnostic methods can help you determine if you have gynaecomastia and what steps to take next.
What Is Gynaecomastia?
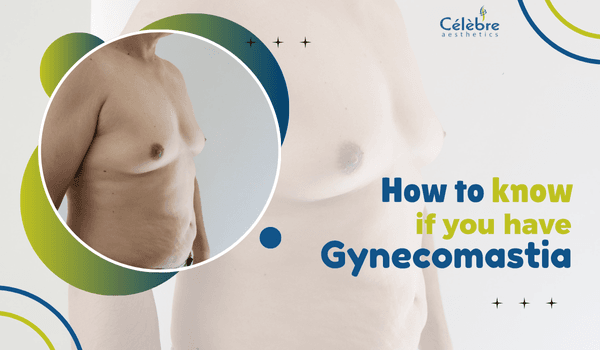
Gynaecomastia is the development of excess glandular tissue in the male chest, resulting in breast enlargement. It differs from chest fat (pseudogynaecomastia), which is caused by excess adipose tissue rather than glandular growth. The condition can affect one or both sides of the chest and may occur at any age due to hormonal imbalances or other underlying factors.Signs and Symptoms of Gynaecomastia
If you are wondering whether you have gynaecomastia, watch for these common symptoms:1. Enlarged Breast Tissue
- A firm or rubbery mass directly under the nipple
- Growth in one or both sides of the chest
- Breast tissue that does not reduce with weight loss or exercise
2. Tenderness or Pain
- Mild to moderate sensitivity around the nipple area
- Occasional pain or discomfort, especially when touching the affected area
3. Changes in Nipple Shape or Size
- Puffy or swollen nipples
- Increased projection of the nipple due to underlying glandular growth
4. Symmetry and Consistency
- Gynaecomastia often presents with firm glandular tissue, whereas chest fat feels soft and spread out
- If only one side is affected or the growth is uneven, a medical evaluation is recommended
Common Causes of Gynaecomastia
Gynaecomastia is primarily caused by a hormonal imbalance between estrogen (which promotes breast tissue growth) and testosterone (which suppresses it). Some of the most common triggers include:1. Hormonal Fluctuations
- Occurs naturally during puberty, aging, or hormonal disorders
- An imbalance between estrogen and testosterone
2. Medications and Drugs
- Certain medications like anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, and some antidepressants
- Recreational drugs such as marijuana, alcohol, and amphetamines
3. Medical Conditions
- Liver disease, kidney failure, or thyroid disorders
- Tumors affecting hormone-producing glands
4. Lifestyle and Dietary Factors
- High soy consumption or processed foods containing phytoestrogens
- Rapid weight gain leading to increased estrogen production
How to Confirm If You Have Gynaecomastia
If you suspect gynaecomastia, it is essential to get a professional evaluation. Here’s how the condition is diagnosed:1. Physical Examination
A doctor will examine your chest, checking for:- The presence of firm glandular tissue vs. soft fat deposits
- Nipple sensitivity or discomfort
- Symmetry and the extent of tissue growth
2. Hormonal and Blood Tests
Blood tests can help identify:- Testosterone and estrogen levels
- Liver, kidney, or thyroid function to rule out medical conditions
3. Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging may be required:- Ultrasound or Mammogram – Helps differentiate glandular tissue from fat
- MRI or CT Scan – If a deeper investigation is needed
When to See a Doctor?
Consult a specialist if:- Your breast enlargement is persistent for more than 6-12 months
- There is significant pain or tenderness
- You notice unusual discharge from the nipples
- The swelling is only on one side (to rule out other conditions)
Treatment Options for Gynaecomastia
If diagnosed with gynaecomastia, treatment will depend on the underlying cause:1. Observation and Lifestyle Changes
- If caused by puberty, it may resolve on its own within a few months to a couple of years
- Reducing alcohol, drugs, or medications that may contribute
- Maintaining a balanced diet and exercise regimen
2. Medications
- Hormonal therapy may be prescribed in some cases to balance estrogen and testosterone levels